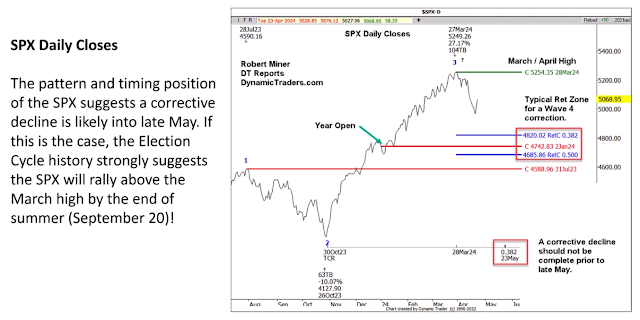
|
| Larry Williams described all of market's action in 8 patterns characterized by direction, contraction and expansion (e.g. HERE) |
In 1990 Toby Crabel published Day Trading With Short Term Price Patterns and Opening Range Breakout. The book is about the fundamental nature of price action, about contraction and expansion, the ebb and flow of price in all markets. Looking at daily bar charts, expect breakouts and / or changes in trend after the following price bar patterns:
Narrow Range (NR): A price bar's range less than the previous bar's range. The opposite of NR is Wide Spread (see below). NR is technically NR2 when
compared to NR4, NR5, and NR7 (see below; more e.g. HERE).
Narrow Range 4 (NR4): A price bar's range less than the previous 3 bars' ranges is the narrowest range in 4 days or NR4.
The opposite is WS4 (see below; more e.g. HERE).
 |
| On Dec 13 (Thu) the E-mini Nasdaq 100 Futures and other US stock indices performed a IDnr4 down day. |
Narrow Range 5 (NR5): A price
bar's range less than the previous 4 bars' ranges is the narrowest range in 5 days or NR5.
The opposite is WS5.
Narrow Range 7 (NR7): A price bar's range less than the previous 6 bars' ranges is the narrowest range in 7 days or NR7. The opposite is WS7 (more e.g. HERE).
Wide Spread (WS): A price bar's range wider than the previous bar's range is a WS. The opposite is NR. WS is technically WS2 when compared to WS4, WS5, and WS7 (more e.g. HERE).
Wide Spread 4 (WS4): A price bar's range wider than the previous 3 bars' ranges is the widest range in 4 days or WS4. The opposite is NR4.
Wide Spread 5 (WS5): A price bar's range wider than the previous 4 bars' ranges is the widest range in 5 days or WS5. The opposite is NR5.
Wide Spread 7 (WS7): A price bar's range wider than the previous 6 bars' ranges is the widest range in 7 days or WS7. The opposite is NR7.
Inside Day (ID): If the high of the current day is lower than the high of the previous day AND the low of the current day is higher than the low of the previous day we have an ID or Inside Day. The opposite is an OD (more e.g. HERE).
Outside Day (OD): If the high of the current day is higher than the high of the previous day AND the low of the current day is lower than the low of the previous day then we have an OD or Outside Day. The opposite is an ID (more e.g. HERE).
Inside Day (ID) and NR4 (IDnr4): An IDnr4 is a combination of an ID and a NR4. This happens when the current day's high is lower than the previous day's high AND the current day's low is higher than the previous day's low AND the range is the narrowest when compared to the previous 3 trading days (more e.g. HERE).
2 Bar Narrow Range (2BNR): The 2-day-range (the higher of the 2 highs less the lower of the 2 lows) is the narrowest 2-day-range in the last 20 trading sessions.
3 Bar Narrow Range (3BNR): The 3-day-range (the higher of the 3 highs less the lower of the 3 lows) is the narrowest 3-day-range in the last 20 trading sessions.
4 Bar Narrow Range (4BNR): The 4-day-range (the higher of the 4 highs less the lower of the 4 lows) is the narrowest 4-day-range in the last 30 trading sessions.
8 Bar Narrow Range (8BNR): The 8-day-range (the higher of the 8 highs less the lower of the 8 lows) is the narrowest 8-day-range in the last 40 trading sessions.
BearHook: A NR with the Open less than the previous bar's Low AND the Close greater than the previous bar's Close (more e.g. HERE).
BullHook: A NR with the Open greater than the previous bar's High AND the Close less than the previous bar's Close (more e.g. HERE).
Stretch: The Stretch is calculated by taking the 10 period SMA of the absolute difference between the Open and either the High or Low, whichever difference is smaller. For example: if Open = 1,250, High = 1,258, Low = 1,240, then take the value of 8 for that day because 1,258 - 1,250 = 8 which is smaller than 1,250 - 1,240 = 10. Then add together all of these values for the last 10 trading days and divide this by 10 to get the 10 day SMA. This value will then become the Stretch. The Stretch is used in calculating where to enter the trade and where to place a stop using the ORB and ORBP trading strategies (see below).
Simple Moving Average (SMA): An SMA is calculated over a number of candles/bars in a chart as the simple average value of that number of bars, e.g. the SMA for the last 10 days closing prices of the DJIA: add together the closing prices for the last 10 days of the DJIA and then divide that by 10 = 10 day SMA. You do not need to use just the closing price to calculate this. You can also use the Open, High, Low, and Close or a combination of any of those, e.g. HLC/3.
Opening Range Breakout (ORB): Using this strategy, a buy stop is placed just above the Open price plus the Stretch and a sell stop just below the Open price minus the Stretch. The first stop triggered enters the trader into the trade and the other stop becomes the protective stop. The earlier in the trading session the entry stop is hit the more likely the trade will be profitable at the close. A market movement that kicks off a trend quickly in the current trading session could add significant profit to a trader's position by the close and should be considered for a multi-day trade. As time passes and we are not filled early on then the risk increases and it becomes prudent to reduce the size of the position during the day. Trades filled towards the end of the day carry the most risk and the later in the day the trade is filled the less likely the trader will want to carry that trade overnight (more e.g. HERE).
Variations of this strategy include the Opening Range Breakout Preference (ORBP): An ORBP trade is a one sided ORB trade. If other technical indicators show a strong trend in one direction then the trader will exercise a "Preference" for the direction in which to trade the ORB trade. A stop to open a position would be placed on the side of the trend only and if filled a protective stop would then be placed. The calculation of where to place the "stop to open" would be the same as that for the ORB trade: For longs, the Open price plus the Stretch and for shorts the Open price minus the Stretch. The ORBP trade is a specialized form of the ORB trade (more e.g. HERE).
Narrow Range 7 (NR7): A price bar's range less than the previous 6 bars' ranges is the narrowest range in 7 days or NR7. The opposite is WS7 (more e.g. HERE).
Wide Spread (WS): A price bar's range wider than the previous bar's range is a WS. The opposite is NR. WS is technically WS2 when compared to WS4, WS5, and WS7 (more e.g. HERE).
Wide Spread 4 (WS4): A price bar's range wider than the previous 3 bars' ranges is the widest range in 4 days or WS4. The opposite is NR4.
Wide Spread 5 (WS5): A price bar's range wider than the previous 4 bars' ranges is the widest range in 5 days or WS5. The opposite is NR5.
Wide Spread 7 (WS7): A price bar's range wider than the previous 6 bars' ranges is the widest range in 7 days or WS7. The opposite is NR7.
Inside Day (ID): If the high of the current day is lower than the high of the previous day AND the low of the current day is higher than the low of the previous day we have an ID or Inside Day. The opposite is an OD (more e.g. HERE).
Outside Day (OD): If the high of the current day is higher than the high of the previous day AND the low of the current day is lower than the low of the previous day then we have an OD or Outside Day. The opposite is an ID (more e.g. HERE).
Inside Day (ID) and NR4 (IDnr4): An IDnr4 is a combination of an ID and a NR4. This happens when the current day's high is lower than the previous day's high AND the current day's low is higher than the previous day's low AND the range is the narrowest when compared to the previous 3 trading days (more e.g. HERE).
2 Bar Narrow Range (2BNR): The 2-day-range (the higher of the 2 highs less the lower of the 2 lows) is the narrowest 2-day-range in the last 20 trading sessions.
3 Bar Narrow Range (3BNR): The 3-day-range (the higher of the 3 highs less the lower of the 3 lows) is the narrowest 3-day-range in the last 20 trading sessions.
4 Bar Narrow Range (4BNR): The 4-day-range (the higher of the 4 highs less the lower of the 4 lows) is the narrowest 4-day-range in the last 30 trading sessions.
8 Bar Narrow Range (8BNR): The 8-day-range (the higher of the 8 highs less the lower of the 8 lows) is the narrowest 8-day-range in the last 40 trading sessions.
BearHook: A NR with the Open less than the previous bar's Low AND the Close greater than the previous bar's Close (more e.g. HERE).
BullHook: A NR with the Open greater than the previous bar's High AND the Close less than the previous bar's Close (more e.g. HERE).
Stretch: The Stretch is calculated by taking the 10 period SMA of the absolute difference between the Open and either the High or Low, whichever difference is smaller. For example: if Open = 1,250, High = 1,258, Low = 1,240, then take the value of 8 for that day because 1,258 - 1,250 = 8 which is smaller than 1,250 - 1,240 = 10. Then add together all of these values for the last 10 trading days and divide this by 10 to get the 10 day SMA. This value will then become the Stretch. The Stretch is used in calculating where to enter the trade and where to place a stop using the ORB and ORBP trading strategies (see below).
Simple Moving Average (SMA): An SMA is calculated over a number of candles/bars in a chart as the simple average value of that number of bars, e.g. the SMA for the last 10 days closing prices of the DJIA: add together the closing prices for the last 10 days of the DJIA and then divide that by 10 = 10 day SMA. You do not need to use just the closing price to calculate this. You can also use the Open, High, Low, and Close or a combination of any of those, e.g. HLC/3.
Opening Range Breakout (ORB): Using this strategy, a buy stop is placed just above the Open price plus the Stretch and a sell stop just below the Open price minus the Stretch. The first stop triggered enters the trader into the trade and the other stop becomes the protective stop. The earlier in the trading session the entry stop is hit the more likely the trade will be profitable at the close. A market movement that kicks off a trend quickly in the current trading session could add significant profit to a trader's position by the close and should be considered for a multi-day trade. As time passes and we are not filled early on then the risk increases and it becomes prudent to reduce the size of the position during the day. Trades filled towards the end of the day carry the most risk and the later in the day the trade is filled the less likely the trader will want to carry that trade overnight (more e.g. HERE).
Variations of this strategy include the Opening Range Breakout Preference (ORBP): An ORBP trade is a one sided ORB trade. If other technical indicators show a strong trend in one direction then the trader will exercise a "Preference" for the direction in which to trade the ORB trade. A stop to open a position would be placed on the side of the trend only and if filled a protective stop would then be placed. The calculation of where to place the "stop to open" would be the same as that for the ORB trade: For longs, the Open price plus the Stretch and for shorts the Open price minus the Stretch. The ORBP trade is a specialized form of the ORB trade (more e.g. HERE).