Narrow range patterns were described by Tony Crabel in his book, "Day Trading with Short Term Price Patterns & Opening Range Breakout". Even though it was published in 1990, many of Crabel's concepts and set-ups are still effective, and in particular his NR4 (Narrow Range 4) and NR7 (Narrow Range 7) patterns became quite popular with short-term traders.
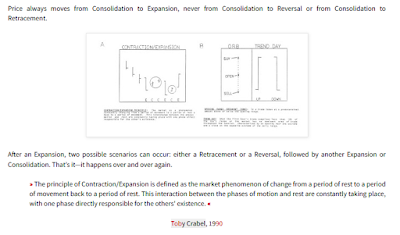
The idea for set-ups is similar to the Bollinger Band Squeeze or Short-Squeezes and Long-Squeezes in general: a volatility contraction is followed by a volatility expansion; narrow range days mark price contractions that precede price expansions. The NR7 day and the NR4
day as such are 'neutral' when it comes to future price direction, and other
tools need to be employed to determine directional bias.
Because NR4/NR7 days are relatively
commonplace and the range is small by definition, the chances of whipsaw
are above average. A break above the NR7 high can fail and be followed
by a break below the NR7 high. Just be aware of this probability and
keep the bigger picture in mind. In other words, be wary of sell signals
within a bullish pattern, such as a falling flag or at a support test.
 |
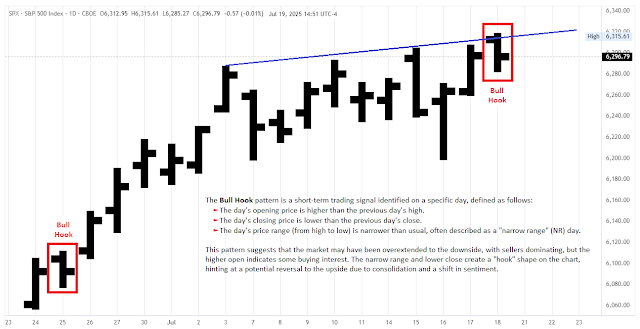
Examples of Narrow Range 7 Inside Days (IDnr7) in the Nasdaq.
|
Traders will want to qualify NR7 signals because they are quite frequent. A typical instrument will produce dozens of NR7 days in a twelve month period and a daily scan of US stocks will often return hundreds of stocks with NR7 days. Traders can increase or decrease the number of narrow range periods to affect the results.
A decrease from NR7 to NR4 would increase the number of instruments fitting the criteria, while an increase from NR7 to e.g. NR20 would decrease the number of signal days. Consider NR7 and NR4 days that are at the same time Inside Days (IDnr4, IDnr7) also as signal days (see chart above).
Strategy: This strategy starts with the day's range, which is simply the difference between the high and the low. Crabel used the absolute range, as opposed to the percentage range, which would be the absolute range divided by the close or the midpoint. Because we are only dealing with four and seven days, the difference between the absolute range and percentage range is negligible.
Crabel focused on two different narrow range timeframes: four days and seven days. An NR4 pattern would be the narrowest range in four days, while an NR7 would be the narrowest range in seven days. It is a very short-term pattern designed to initiate a trade based on an "Opening Range Breakout", which is another term from Crabel's book. Look for an upside breakout when prices move above the high of the narrow range day and a downside breakdown when prices move below the low of the narrow range day.
Bull Signal:
- The daily bias is bullish.
- Identify a NR4, a NR7, an IDnr4 or an IDnr4 day.
- Buy on move above high of narrow range day high.
- Set trailing stop-loss.
Bear Signal:
- The daily bias is bearish.
- Identify a NR4, a NR7, an IDnr4 or an IDnr4 day.
- Sell on move below low of narrow range day low.
- Set trailing stop-loss.
Targets: Because this is a short-term setup, it is important that the trade starts working right away. Failure to continue in the direction of the signal is the first warning. After a buy signal, a move below the low of the narrow range day would be negative. Conversely, a move above the high of the narrow range day would negate a sell signal. Consider profit targets and stop-losses.
Crabel took profits quite quickly, usually at the close of the first trading day or on the first profitable close. Again, this is very short-term-oriented and might not be suitable for all traders. Alternatively, profits can be taken near the next resistance levels or a percentage target can be used. Base stops on previous highs and lows, the Average True Range (ATR), etc. For example, the stop-loss on a long position could be set two ATR values below current prices and trailed higher.

.png)


.png)




















