Saturday, July 19, 2025
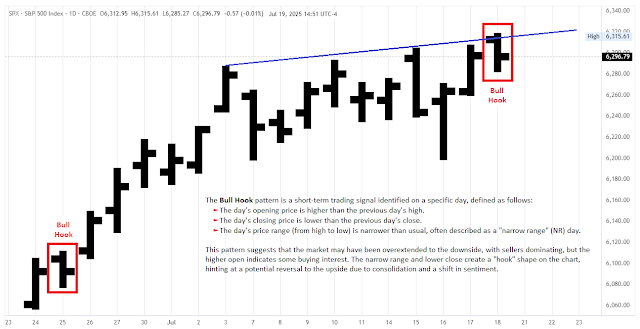
"Bull Hook" Toby Crabel Price Pattern in the S&P 500
Sunday, July 13, 2025
"8 Bar Narrow Range" (8BNR) Toby Crabel Price Pattern in the NASDAQ
Short Trade: Place a sell stop order at the open price minus the stretch.
Like all technical patterns, the 8BNR is not foolproof. False breakouts, market noise, or unexpected events can lead to losses. Traders should avoid mechanical application and incorporate additional technical or fundamental analysis to confirm signals. Always combine the pattern with other market analysis for best results.
Wednesday, June 26, 2024
2-Bar Narrow Range Setup | Toby Crabel
Because it is not dependent on a constant measurement it represents contraction in a volatile or narrow market period. In other words, contraction is a relative condition that can occur even in a volatile market. Once a market concept is formulated it is tradable. An ORB (Opening Range Breakout) trade is taken the day after the 2-Bar NR formed. An ORB trade is entered at a predetermined amount above or below the opening range (stretch), that is the range of prices that occur in the first 30 seconds to 5, 15 or 30 minutes of trading.
Friday, June 14, 2024
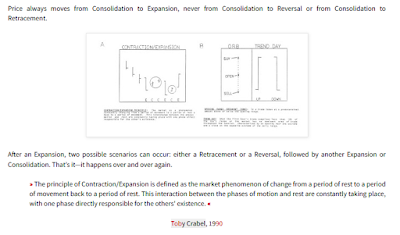
The Principle of Contraction/Expansion | Toby Crabel
After an Expansion, two possible scenarios can occur: either a Retracement or a Reversal, followed by another Expansion or Consolidation. That’s it—it happens over and over again.
NR7 - A day with a daily range that is narrower than the previous six day’s daily ranges compared individually.
WS4 - (Widespread 4) A day with a daily range that is larger than any of the previous three day’s daily ranges.
WS7 - (Widespread 7) A day with a daily range that is larger than any of the previous six day’s daily ranges
Isaac Newton's 'First Law of Motion', 1687
Sunday, June 9, 2024
An Outside Look at Inside Days | Larry Williams
There does seem to be some validity to this. The following chart shows what happens when we have an inside day with a down-close while prices are lower than they were 10 days ago. In the Standard and Poor’s, 71% of the time you were higher the next day. This may not even be as significant as the fact that 71% of the time you were higher 20 days after this occurrence. In the Value Line, price is higher 50% of the time after the occurrence, and in Treasury Bonds it’s higher 75% of the time. The pattern in Silver was not nearly as bullish, which surprises me because I had used this trading technique in Silver with some success … which just goes to show you! In Silver, on 36% of the time you were higher 20 days following the occurrence of the pattern. Soybeans were higher 57% of the time, Bellies 50% of the time and the Swiss Franc, where so far we have not found a pattern that forces prices higher, you were up only 22% of the time.
For a moment though, let’s take a look at just the occurrence of an inside day. What happens when we simply have an inside day with a down-close? Does that, on its own merit, forecast any significant market activity? The results are on the next few pages [of 'The Future Millionaire's Confidential Trading Course']. What can you find?
Then there’s the other side of this coin. What happens if we have an inside day with an up-close? Does this forecast positive action? It appears that it does to some extent. Study the tables for yourself. I have gone to the computer to give you the results for almost all possible configurations of the inside days. While, quite frankly, much of the data suggests random-gibberish-behavior, others are relationships that you can find and successfully trade with. What you need to focus on here is not that the patterns will always work for you, but that patterns, like methods, systems and tools, will give you the much needed odds that lead to successful speculation.
Sunday, February 19, 2023
Point & Line | Charles Drummond

- prices each day moved a maximum of "x" mm away from the ‘dot' line.
- prices each day, moved a maximum of "x" cents up or down from the dot itself.
- prices eventually stop moving above the main line in an up market into an area or channel just under the line, and in an up moving market, prices are topping.
- the dots started to move closer and closer together in an upmarket and the market was topping.
- dots swung off the main dot line - bells ringing left and right - market is topping.
- the dot is swinging more, it's falling under or above. The dot didn't swing under or above. And since it didn't, and not doing what it's supposed to do, the opposite is happening.
- instead of the dot going up exactly in a straight line, or down in a straight line, they are "snaking" very close to each other, horizontally - we're in a congestion.
Charles Drummond (1979) - How to make Money in the Futures Market ... and lots of it.
Ted Hearne (2007) - Drummond Geometry: Picking Yearly Highs and Lows in Interbank Forex Trading.
Tuesday, July 5, 2022
Inside Days in the S&P 500 │ Toby Crabel
Toby Crabel (1990) - Computer studies suggest that Inside Days (ID) provide very reliable entries in the S+P market. The data used in the studies is daily open, high, low and close prices from 1982 to 1987. All of the following patterns are defined for a computer but can be seen easily on a daily bar chart.
- Pattern (1) is simply an inside day followed by a sale (s) on a lower open or buy (b) on a higher open. Entry is on the open with an exit on the same day's close with no stop. This procedure produced sixty-eight percent winning trades with profits of $18,000 after an $18 commission. This is a reasonably high percentage and suggests a strong bias in the direction of the open after any ID.
- Pattern (2a) is defined as an ID with a higher close than the previous day followed by a higher open. A buy is taken on the open and exited on the close. The same is done on the sales (Pattern (2b)) if there was an ID with a lower close followed by a lower open. Again, stops were not used. There were forty-four trades as such with seventy-four percent of them profitable. Net profit was $14,914. The percentage has improved and profits are better per trade than Pattern (1). This supports the premise that the closing effects the next day's action and potential breakout. Further tests uncover some variations to above results. Although the opening direction after an inside day appears to be a valid indicator of upcoming direction, there are same specific patterns that show very high percentage profitability without the use of the previous day's closing direction. Specifically, two patterns; one a sale (Pattern (3)), one a buy (Pattern (4)).
- Pattern (3): The day of entry is called Day 1. The day of immediately preceding the entry is Day 2 and each preceding day - 3, 4, 5, etc. On Day 1 an open lower than Day 2's mid-range and lower than Day 2's close is necessary. Day 2 must be inside of Day 3. Day 3 must have a higher low than Day 4. A sale is made on the open of Day 1 with exit on the close of Day 1. Profits were eighty percent with winning trades five times the size of losing trades. The only shortcoming is that only ten trades could be found from 1982-1987.
- Pattern (4) is similar to Pattern (3) with opposite parameters. The only exception is the open on Day 1 need only to be higher, not above mid-range. So to review Pattern (4), Day 1 a higher open than Day 2. Day 2 inside Day 3. Day 3 lower high than Day 4. Results were as follows: Ninety-one percent profits; 860 to 820 average winner to average loser. No stops were used. Only eleven patterns to the upside were found.
The market action implied in each pattern is a short-term trend with a loss of momentum on the Inside Day. The open on Day 1 is in the opposite direction of the trend and is an indication of a shift in sentiment. This shift in sentiment causes those who still have existing positions against the opening direction to liquidate longs or cover shorts. Participants covering their positions is more than enough to tip off a directional move.
A slightly different perspective on the same type of pattern is to look for a retracement to the previous day's close after the opening and take a position at that point in the direction of the open. I tested four patterns to demonstrate this principle.
- Pattern (5) shows an Inside Day with a lower close on Day 2 than Day 3. Day 1's open is above Day 2's close. The chances are sixty-two percent that the market will close above Day 2's close on Day 1.
- Pattern (6) is an Inside Day on Day 2 with a higher close than Day 3. Day 1's open is above Day 2's close. The chances are seventy-nine percent that the market will close above Day 2's close on Day 1.
- Pattern (7) shows an Inside Day on Day 2 with a lower close than Day 3's close. Day 1's open is below Day 2's close. The chances are fifty-nine percent that the close on Day 1 will be lower than Day 2's close.
- Pattern (8) shows an Inside Day on Day 2 with a higher close than Day 3's close. Day 1's open is below Day 2's close. There is a sixty-seven percent chance that the market will close below Day 2's close on Day 1.
How can you use this information? It suggests a strong bias in the direction of the open especially after a higher open. The prolonged bull market obviously had an impact on these results but in general, a counter move back to Day 2's close after the opening direction is known, should be observed for a loss of momentum and possible entry in the direction of the open.
Another totally different test in the S+P has same interesting implications and could be tied in with the previous patterns. On any day that the market has moved two hundred points above the open intra-day, it has closed above the open ninety percent, of the time. Also, on any day that the market has moved two hundred points below the open it has closed below the open eighty-eight percent of the time. This was during the period from 1982-1988.
An application of these results is as follows: Enter in the direction of the initial trend on any low momentum move back to the open and exit on the close of the session. This can be done after the initial trend is established with a two hundred point move in one direction off the open. The main qualification is price action on the pullback. A high momentum move back through the open leaves the initial two hundred point move in question. This can also be applied after an Inside Day very effectively.
I think it is necessary to shed light on how extraordinary the results for Inside Days are: A test on a sale of a higher open or buy of a lower open with no other information to work with provides a winning trade fifty-six percent of the time when exiting on the close the same day of entry. This suggests a natural tendency for the market to reverse the opening direction by the time of the close.
This natural tendency is reversed after an ID. Why? What is it about an ID that produces follow through after the open? An ID is narrower than the previous day. Any narrowing day shows loss of momentum and when within a previous day's range it forms a congestion area. A congestion is directionless trade with the market searching for new information. A temporary state of balance or equilibrium exists.
There is a tendency for the market to trend after a congestion. If an Inside Day is a valid congestion, it will produce an imminent trend day. One can assume from the above tests that there is a tendency to trend after these patterns (ID). These tests support the premise that Inside Days are valid congestion areas. It appears that market participants act on the first piece of information indicating trend after the Inside Day - the open. Also, the direction of the close on the ID will provide further clues on the direction of the breakout when added to the information of opening direction. The increase in percentage profit and relative profits when these variables are added supports this conclusion.
Why do these indications work so well in the S+P? The S+P generally is an urgent market. The distinguishing characteristic of this market is its tendency to trend throughout the session. This market is notorious for big, fast moves intra-day. Peter Steidlmayer (Markets and Market Logic) calls it a One-Time Frame market. One may reason that in a One-Time Frame market the inside day is a more reliable indication of upcoming trend than in a Two-Time Frame market. The market principle that is in force is contraction/expansion. The Inside Day is contraction, and in a One-Time Frame market 1-Day contraction is all that is necessary to tip off a directional move.
In summary, the above tests suggest that an Inside Day is a valid congestion area and it follows that all breakout rules for congestion areas should be implemented after an Inside Day forms. The resulting breakout is expansion.
 |
| Three-Bar Inside Bar Pattern by Johnan Prathap - HERE & HERE |
[...] The Principle of Contraction / Expansion is defined as the market phenomenon of change from a period of rest to a period of movement back to a period of rest. This interaction between the phases of motion and rest are constantly taking place, with one phase directly responsible for the others' existence. A Trend Day is defined as a day when the first hour's trade comprises less than 10% of the day's range or the market has no dominant area of trade throughout the session. Trend days are characterized by an opening near one extreme and a close on the opposite extreme of the daily range. Trend days fall into the category of expansions. Congestion is a series of trading days with no visible progress in either direction. Usually associated with narrow range days or non-trend days. Contraction is a market behavior represented by a congestion or dormant period either short-term (ID) or long-term narrow range (8 Bar NR) and usually reaching its narrowest phase at the end of the period.