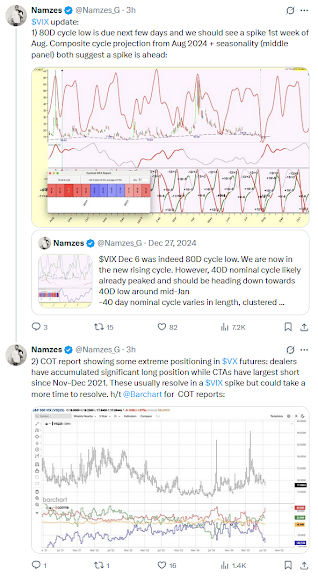
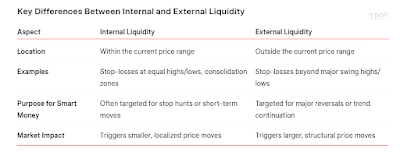
This one pattern helped me make over $4 million in the last three years and even break the world-record payout at Apex. Let me show you exactly how it works:
» For a true engulfing pattern, the new candle must break the
previous candle’s low and the previous candle’s high. «
What Is an Engulfing Bar? We’re
simply looking for two candles—along with proper context—to define the
pattern: Imagine we have a down candle with its open, high, low, and
close. The next candle is what determines whether we have an engulfing
bar. For a true engulfing pattern, the new candle must break the
previous candle’s low and the previous candle’s high. It completely “engulfs” the previous range (aka Outside Bar/Candle).
Understanding the Context: Inside a higher-timeframe candle (4-Hour or daily), there are dozens of smaller candles—1-minute, 5-minute, 15-minute—that form all the micro-structure. Within that lower-timeframe structure, the engulfing pattern represents:
▪ A Market Maker Buy Model (for bullish engulfing)
So although it's only two candles on a higher timeframe, those two candles often reflect an entire lower-timeframe reversal model.
The key is the closure. Many beginners think a candle will close as an engulfing bar, only for it to close weakly or back inside the prior range. That invalidates the pattern. A proper engulfing bar should close with a strong, decisive body—typically in the upper 50% for bullish setups, or the lower 50% for bearish setups.
Bullish vs. Bearish Examples: For a bullish engulfing bar, the second candle runs below the prior low, reverses, and breaks the prior high (Outside Candle). For a bearish engulfing bar, it runs above the prior high, reverses, and breaks the prior low. Both reflect a higher-timeframe representation of a lower-timeframe Market Maker Model.
What Most Traders Don’t Realize: Every setup—Engulfing Bars, Fair Value Gaps (FVGs), Market Maker Models—has a failure rate. I learned this the hard way after blowing dozens of accounts trying to trade every engulfing bar I saw. Two things matter:
-
Every setup fails sometimes. If you backtest these candles, you'll see some of them lose. Your job is not to find the magical 100%-win-rate setup. It doesn’t exist. You may find these patterns work 60% of the time. Your winners must be managed well enough to pay for the losers.
-
Location matters. A lot. When I was new, I took every engulfing bar. That was a huge mistake.▪ If you're bullish, you want the engulfing bar to form at a swing low, ideally after taking out sell-side liquidity.▪ If it forms after taking out buy-side liquidity—at a high—it's often a sign of exhaustion and more likely to fail.▪ The reverse is true for bearish setups.
Avoid:
▪ Bullish engulfing bars printed at or after taking out buy-side liquidity.
▪ Bearish engulfing bars printed at or after taking out sell-side liquidity.
These filters alone drastically improve your win rate.
The $98,000 Example: Let’s walk through the trade from last week. We printed a large bullish engulfing candle immediately after FOMC. The candle swept sell-side liquidity, reversed, broke the prior high, and closed strongly—exactly what we want at a swing low. We were also inside a daily Fair Value Gap (FVG), adding even more confluence.
My first target was buy-side liquidity above the highs. Since the market was near all-time highs, I was also looking for a move toward the psychological 25,000 level. As soon as the futures market reopened at 6 p.m., I entered with a 20-lot position. My stop was below the weekly open. I was looking for roughly a 1:3 risk-to-reward.
On the lower timeframes, the price action continued to confirm the model—bullish FVGs forming on the way up, continuation structure holding. Meanwhile, bearish engulfing candles printed at swing lows failed, exactly like we want to see.
I showed the live account login on the video: real balance, real fills, floating around $93,000 at one point. But the dollar amount doesn’t matter. If your account is small, making $200 or $400 using the same rules is identical—it’s just a matter of position size. Years ago, I was risking $500–$1,000. As my net worth grew, I increased my risk proportionally. Eventually, price hit my target and I closed the trade for roughly $98,000.
Final Thoughts: Engulfing bars are easy to spot—but only powerful when combined with
▪ Proper context
▪ Liquidity understanding
▪ Market structure
▪ Higher-timeframe narrative
▪ Disciplined trade management
Your homework is to backtest and forward-test these exact setups: where the engulfing bar forms, where the liquidity sits, where your stop should go, and how to trail it as price moves in your favor. Scaling in, adjusting stops, and managing the trade all revolve around that one pattern.
With this engulfing bar strategy and the rules I just shared, you now have everything you need to start identifying high-probability opportunities. Remember: profitable trading isn’t about talent or luck—it’s about discipline, patience, and following your rules every single time.
Reference:
See also: