S&P 500 E-mini Futures (weekly candles) vs Tri-Annual Pivot Levels (for 2022-2024).
Based on spectrum analysis, Sergey Tarassov forcasted a multiyear high in US-stocks sometime around August 2024 between the crests of the 40 Month Cycle and the 42 Month Cycle.
By then the tri-annual R1 level at 6,019 could well be reached. R2 is at 6,928.
S&P 500 E-mini Futures (weekly candles) vs Yearly Pivot Levels (for 2024).
Tri-Annual and Yearly Pivot Points and Levels are suitable for long-term investing or swing trading
with a time frame of several months to a year or more.
S&P 500 E-mini Futures (weekly candles) vs Quarterly Pivot Levels (for Q3 July-September 2024).
Quarterly Pivot Points and Levels are suitable for medium-term trading with a time frame of several
weeks to a few months. They are useful for identifying intermediate support and resistance levels,
trend continuations, and potential corrections.
.
S&P 500 E-mini Futures (daily candles) vs Monthly Pivot Levels (for (July 2024).
Monthly Pivot Points and Levels are ideal for short-term to medium-term trading
with a time frame of several days to a few weeks.
S&P 500 E-mini Futures (daily candles) vs Weekly Pivot Levels (for July 07-12, 2024).
Weekly Pivot Points and Levels are suitable for short-term trading with a time frame of one to several
days to a week, to identify short-term support and resistance levels, trend continuations, and potential reversals.
S&P 500 E-mini Futures (4 hour candles) vs Daily Pivot Levels (for July 10, 2024).
Daily Pivot Points and Levels are ideal for short-term and intraday trading with a time frame of several hours to a day in order to identify short-term support and resistance levels, trend reversals, and potential breakouts. Daily Pivots can be used to make quick trading decisions, adjust stop-losses, or set price targets for the current trading session.
Pivot Points, Support and Resistance levels are calculated based on previous high, low, and close prices. These levels can identify areas, where price may bounce, reverse or break through, and where to set entry, stop-loss and take-profit orders. This technique is valid on various timeframes. Common types are Floor (Trader) Pivots a.k.a. Standard or Traditional Pivots (= all charts above), Central Pivot Range (CPR), Fibonacci, Woodie, Classic, Camarilla and DeMark Pivot Points, each type having their own calculation method.
See also:
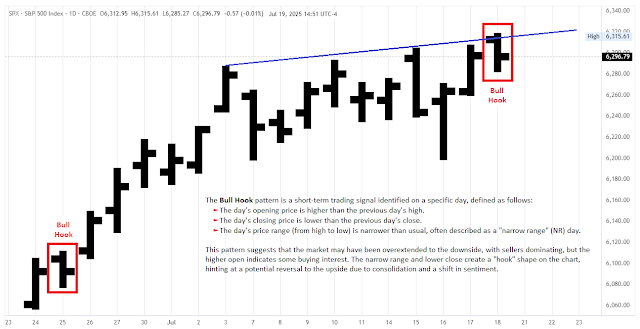

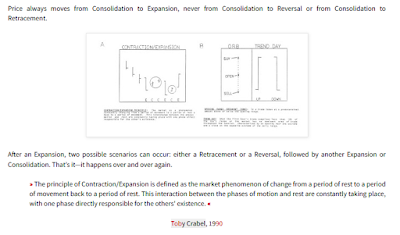












+-+January11,+2016%20conv%2012.png)

+-+January11,+2016%20conv%2013.png)




+-+January11,+2016%20conv%2015.png)
+-+January11,+2016%20conv%2014.png)

+-+January11,+2016%20conv%2016.png)
+-+January11,+2016%20conv%2017.png)









