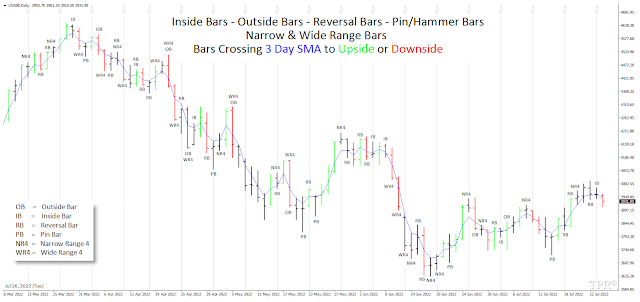
A day in which there is a new high followed by a lower close
is a downwards reversal day (RB). An upwards reversal day is a new low followed by a
higher close. A reversal day by itself is not significant unless it can be put
into context with a larger price pattern, such as a clear trend with sharply
increasing volatility, or a reversal that occurs at the highest or lowest price
of the past few weeks. Short-term reversals are likely after wide-ranging (WR4) and narrow-ranging days (NR4), especially when the open, high, low and close of the daily price bar are altogether above or below of a simple three-day moving average line of daily close prices.
A wide-ranging day is likely to be the result of a price shock, unexpected news, or a breakout in which many orders trigger one another, causing a large increase in volatility. A wide-ranging day could turn out to be a spike or an island reversal. Because very high volatility cannot be sustained, a wide-ranging day will likely be followed by a reversal, or at least a pause. When a wide-ranging day occurs, the direction of the close (if the close is near the high or low) is a strong indication of the continued direction. An outside day (OB) often precedes a reversal. An outside day can also be a wide-ranging day if the volatility is high, but when volatility is low and the size of the bar is slightly longer than the previous bar, it is a weak signal. As with so many other chart patterns, if one day has an unusually small trading range, followed by an outside day of normal volatility, there is very little information in the pattern. Context and selection are important.